A quadrantal angle is one that is in the standard position and has a measure that is a multiple of 90° (or π/2 radians) A quadrantal angle will have its terminal lying along an x or y axis In the figure above, drag the point A around and see which angles are quandrantal anglesAnd a quarter revolution is π⁄2 radians See the animation in figure 8a and the illustration in figure 9b Figure 8 One radian is the angleHow do you find the radian measure of an angle of 280?
Radian Measure Topics In Trigonometry
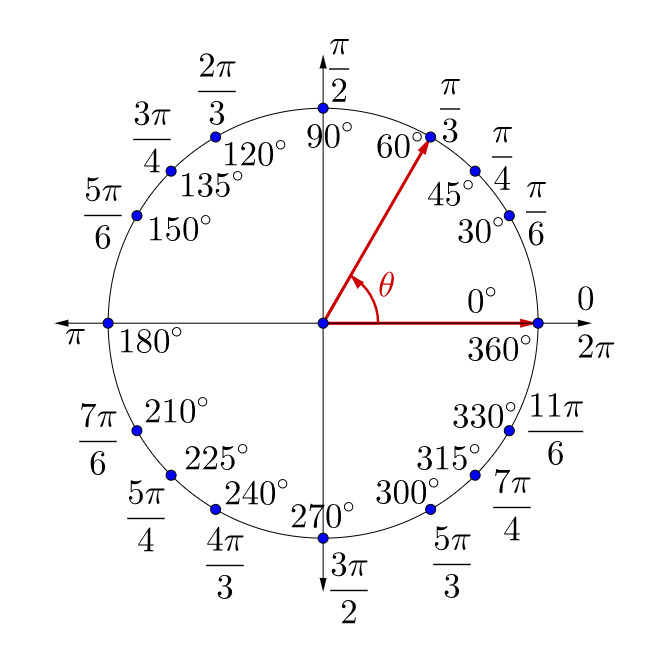
π 2 radian angle in standard position
π 2 radian angle in standard position-And radian measures of special angles in the first quadrant and for 90 2 π °= radians All other special angles shown are multiples of theses angles Arc Length and Area of a Sector The arc length s and area A of a sector with radius r and central angle θ (measured in radians) are as follows Arc length s = rθ Area 2 1 2 A = r θ Notes 0 · Radian and degree measure 1 TRIGNOMETRIC FUNCTIONS 1 Radian and Degree Measure 2 2 3 Angle formed by rotating a ray about its endpoint (vertex) Initial Side Starting position Terminal Side Ending position Standard Position Initial side on positive xaxis and the vertex is on the origin


Webpage Of Dr Tom Cuchta
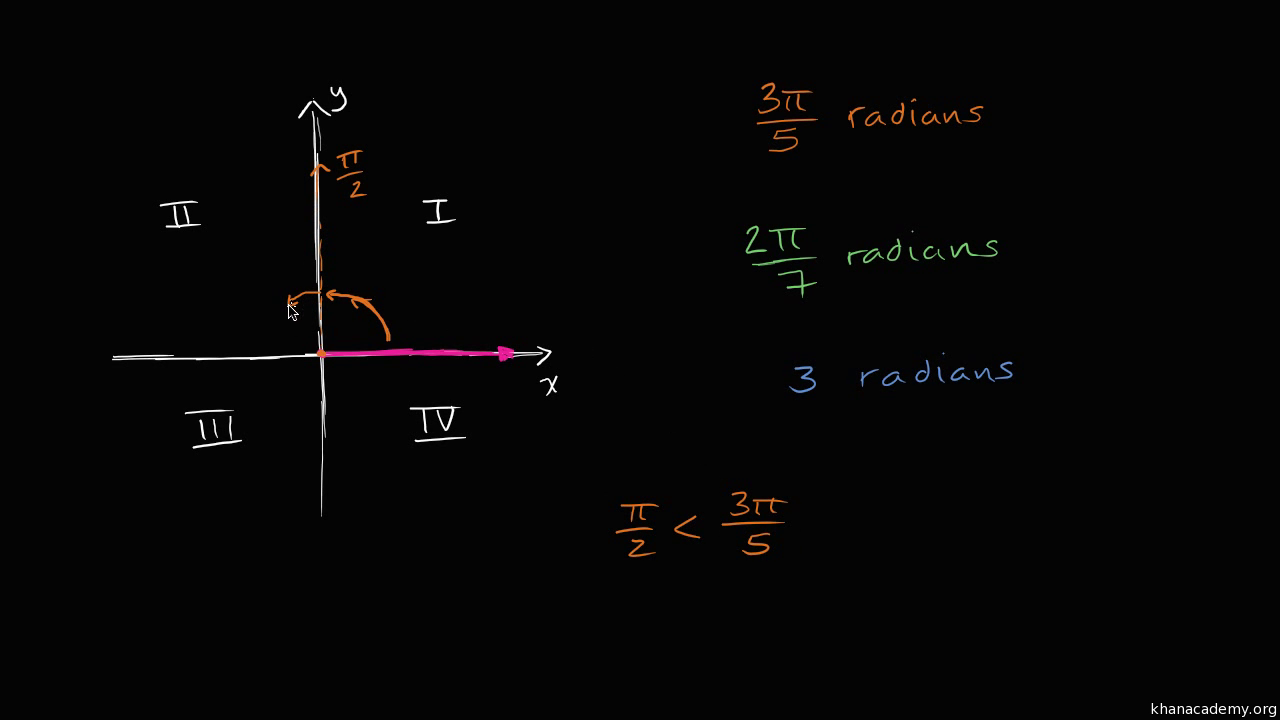
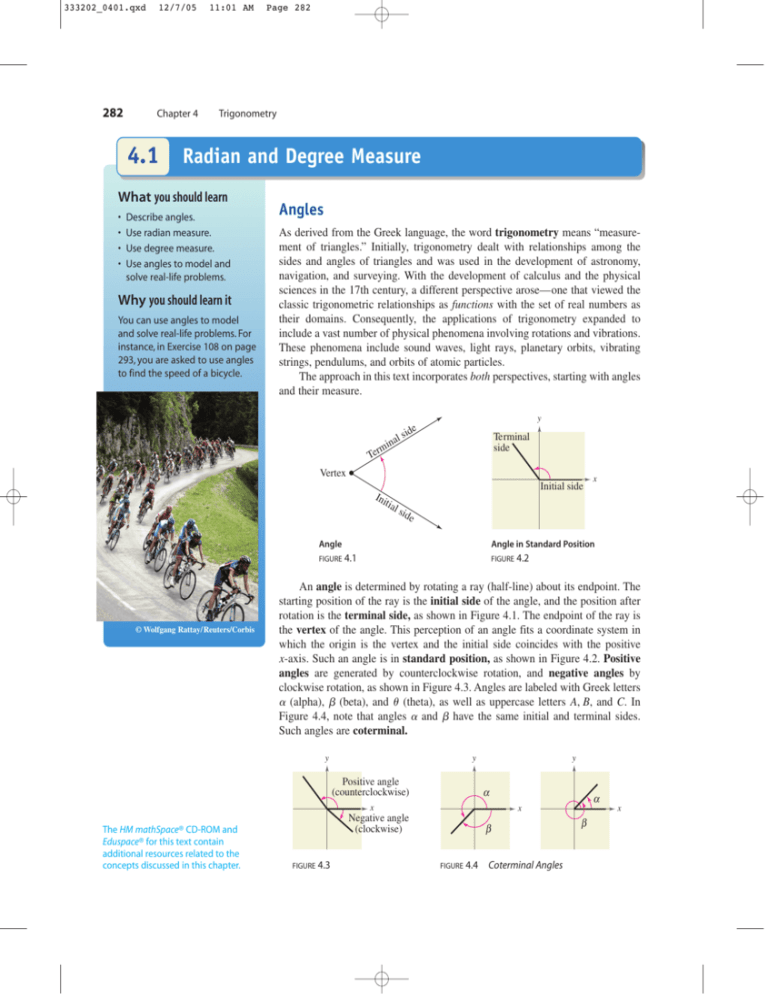
· An angle is in "standard position" when the vertex is at the origin and the initial side of the angle is along the positive xaxis A Positive angle measured in counter clockwise direction from the Horizontal (xaxis) Thus, the initial side of the angle 3π 4 is coincides with Positive side2 π radians = 360 ∘ π radians = 360 ∘ 2 = 180 ∘ 1 radian = 180 ∘ π ≈ 573 ∘ 2 π radians = 360 ∘ π radians = 360 ∘ 2 = 180 ∘ 1 radian = 180 ∘ π ≈ 573 ∘ Note that when an angle is described without a specific unit, it refers to radian measureDetermine the coterminal angle of π/4 Solution Given Angle θ = π/4, Which is in radians, So, multiples of 2π add or subtract from it to compute its coterminal angles Now, subtract 2π from the angle = π/4 − 2π = −7π/4 Hence, the coterminal angle of π/4 is equal to −7π/4 Example 2
Play this game to review Precalculus Estimate the angle to the nearest onehalf radian Preview this quiz on Quizizz Quiz QUIZ Radian Measure and Standard Position DRAFT 11th 12th grade Played 2 times 90% average accuracy Mathematics 8 days ago by beth_hancock_ 0 Save Edit Edit QUIZ Radian Measure and Standard PositionHow to Find a Reference Angle in Radians Finding your reference angle in radians is similar to identifying it in degrees 1 Find your angle For this example, we'll use 28π/9 2 If your angle is larger than 2π, take away the multiples of 2π until you get a value that's smaller than the full angleDivide the angle in radians by the number of time units elapsedlatex\,\omega =\frac{\theta }{t}/latex The resulting speed will be in radians per time unit Finding Angular Speed A water wheel, shown in , completes 1 rotation every 5 seconds To draw an angle in standard position
· 1) Draw an angle in standard position Label the vertex, initial side, and terminal side 2) Explain why there are an infinite number of angles that are coterminal to a certain angle 3) State what a positive or negative angle signifies, and explain how to draw each 4) How does radian measure of an angle compare to the degree measure?A radian is the angle where the arc length equals the radius One revolution equals 2π radians;2 π radians = 360° π radians = 360° 2 = 180° 1 radian = 180° π ≈ 573° 2 π radians = 360° π radians = 360° 2 = 180° 1 radian = 180° π ≈ 573° See Figure 11 Note that when an angle is described without a specific unit, it refers to radian measure



Radian Measure Topics In Trigonometry


Radian Measure Including How To Convert Radians To Degrees And The Trigonometric Functions Of Special Angles
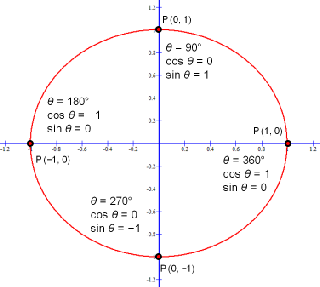
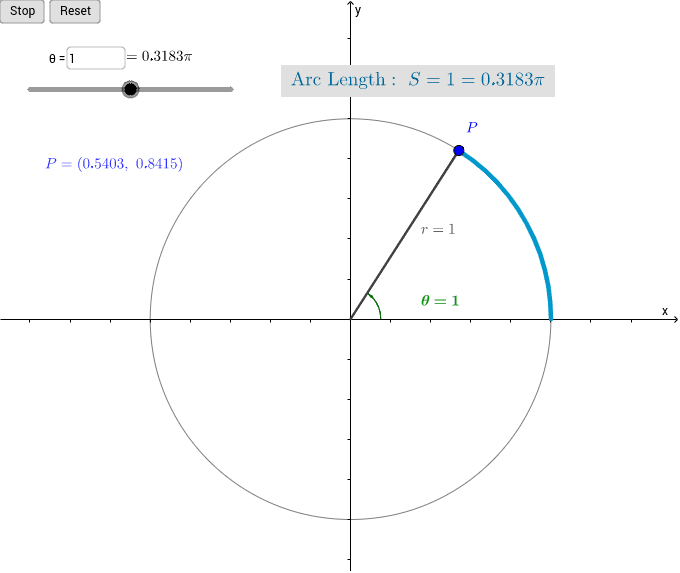
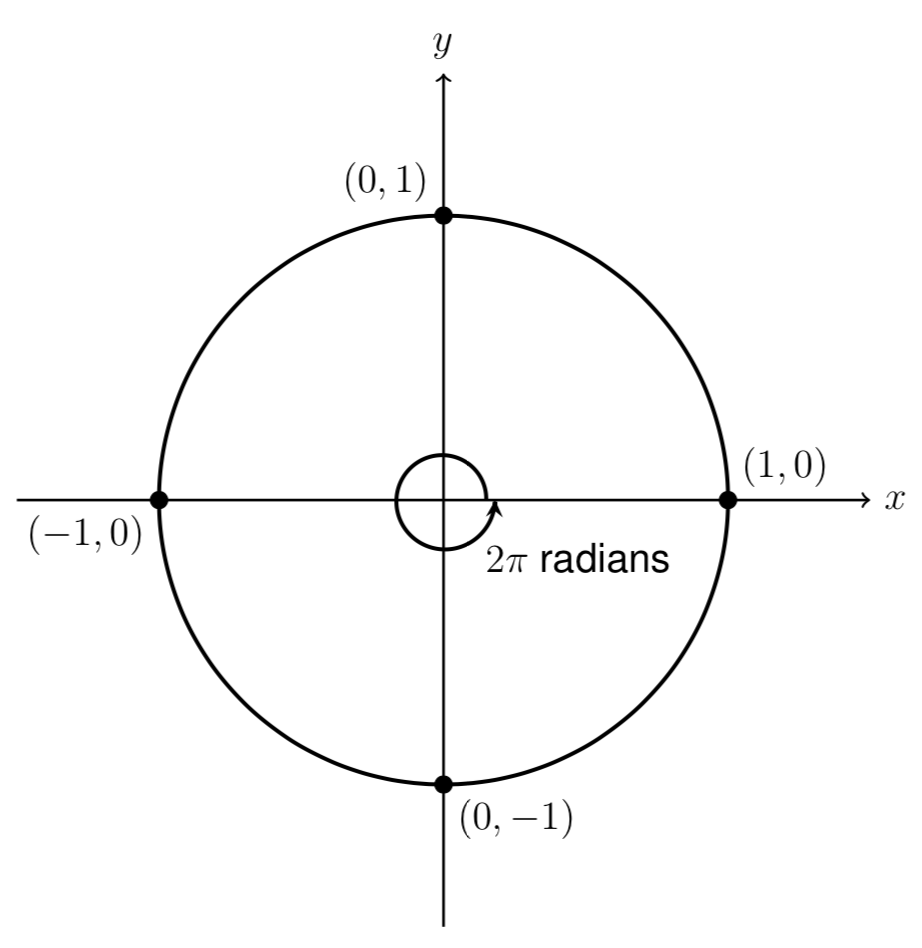
An angle in standard position whose terminal side intercepts an arc of length r Because the circumference of a circle is 2πr, there are 2π radians in a full circle So, degree measure and radian measure are related by the equation 360° = 2π radians, or 180° = π radians STUDY TIP If two angles differ by a multiple of 360°, then theSo, by the example above and the fact that a circle is 360o, we see that 2π radians = 360o or π radians = 180o To convert from degrees to radians, multiply degrees by π rad o/ 180 (πA = n / 2 sin τ / n A = n / 2


Angles Precalculus Ii


Radian Angles Quadrants Video Radians Khan Academy
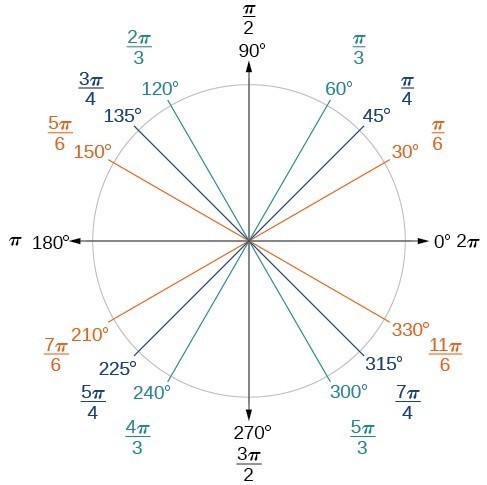
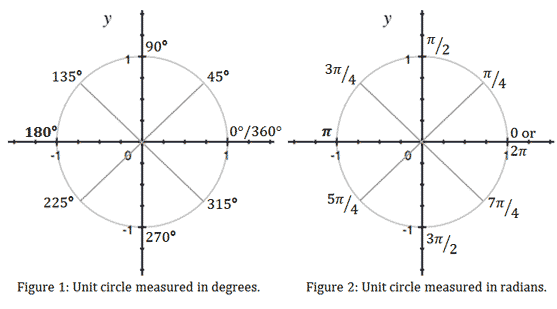
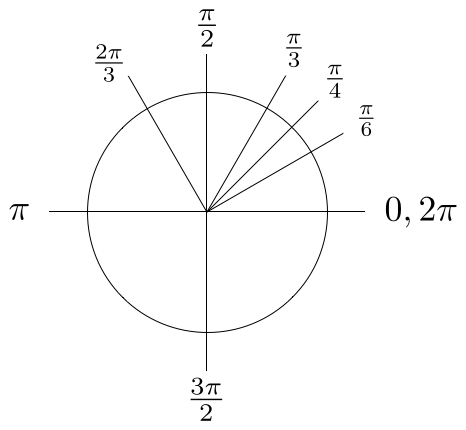
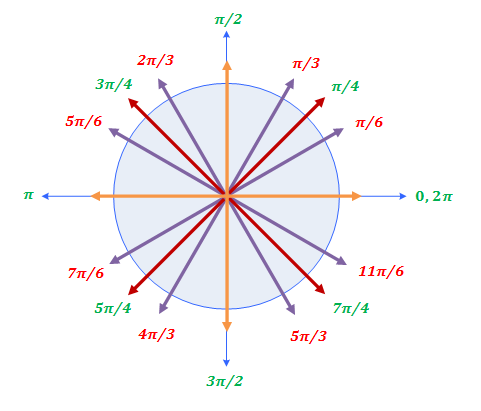
2π π 4, 2 2 2 4 Question Find the radian measure of the angle with the given degree measure rad 18 The measure of an angle in standard position is given Find two positive angles and two negative angles that are coterminal with the given angle (Enter your answers as a commaseparated list)π 2 radians The quadrants and some quadrantal angles (For convenience, we may label a standard angle by labeling its terminal side) Example What quadrant does 5π 6 lie in?Angles drawn in standard position that share a terminal side are called coterminal angles The radian measurements of coterminal angles always differ by an integer multiple of 2π 2 π and angles whose radian measurements differ by an integer multiple of


Exam 2 Review Key


The Unit Circle
Regents Exam Questions FTF Unit Circle Name _____ wwwjmaporg 3 10 On the unit circle shown in the diagram below, sketch an angle, in standard position, whose degree405° (a) Draw the angle in standard position (b) Convert to radian measure using exact values rad (c) Name the reference angle in both degrees and radians °π radians 4 180 π radians 180 45 4 4c Convert 2 π radians to degrees 4d Convert 6 radians to degrees 6 radians 180 π radians 1080 3438 π 4d Convert 2 radians to degrees Round to two decimal places Objective #5 Draw angles in standard position Solved Problem #5 5a Draw the angle 4 π θ in standard position Since the angle is


Trigonometry Facts The Amazing Unit Circle


How Do You Find The Six Trigonometric Functions Of 3pi 2 Degrees Socratic
What is the measure in degrees of the angle #A=(7pi)/6#?In which quadrant is the terminal of an angle in standard position whose measure is #(55pi)/3#?(Through what quadrant does the terminal side pass when the angle is in standard position?) Solution Observe 3π 6 = π 2 < 5π 6 < 6π 6 =π , so 5π 6 is in Quadrant II


2 Pi Or Not 2 Pi Wolfram Blog


Radian And Degree Measure
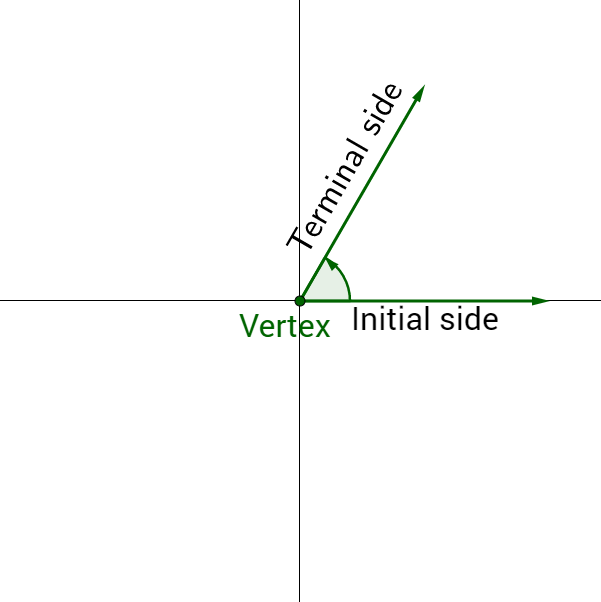
Standard Position of Angles Degrees and Radians DRAFT 3 years ago by moconno2 9th 12th grade Mathematics 1/2 π 1 π alternatives 2π 1/2 π Q angle in standard position with teminal ray on an axis answer choices quadrantal angleAn angle is in standard position if its vertex is located at the origin, and its initial side extends along the positive xaxis See Figure 5 Figure 5 (360°) equals 2 π 2 π radians A half revolution (180°) is equivalent toThe 1 / 2 more clearly expresses that area is the integral of circumference;



Web Lesson Radian Angle Measure


Biomath Trigonometric Functions
A half revolution is π radians; · color(purple)(pi / 4 is the coterminal angle of (9pi)/4 between (0, 2pi) The coterminal angle is to be between 0 & 2pi Given angle (9pi) / 4 We will subtract 2pi to get the coterminal angle (9pi) / 4 2pi = (9pi) / 4 (8pi) / 4 = color(purple)(pi / 4Math 1330 Section 43 Unit Circle Trigonometry An angle is in standard position if its vertex is at the origin and its initial side is along the positive x axisPositive angles are measured counterclockwise from the initial sideNegative angles are measured clockwiseWe will typically use the Greek letter θ to denote an angle



How To Convert Between Degrees And Radians Studypug


Cochranmath Coterminal And Reference Angles
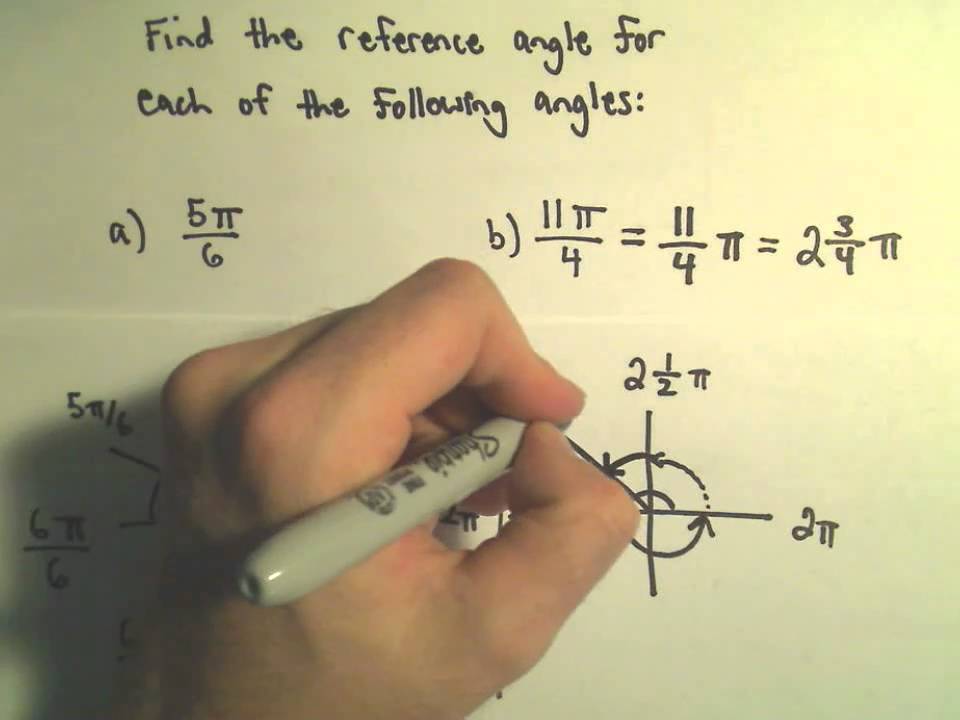
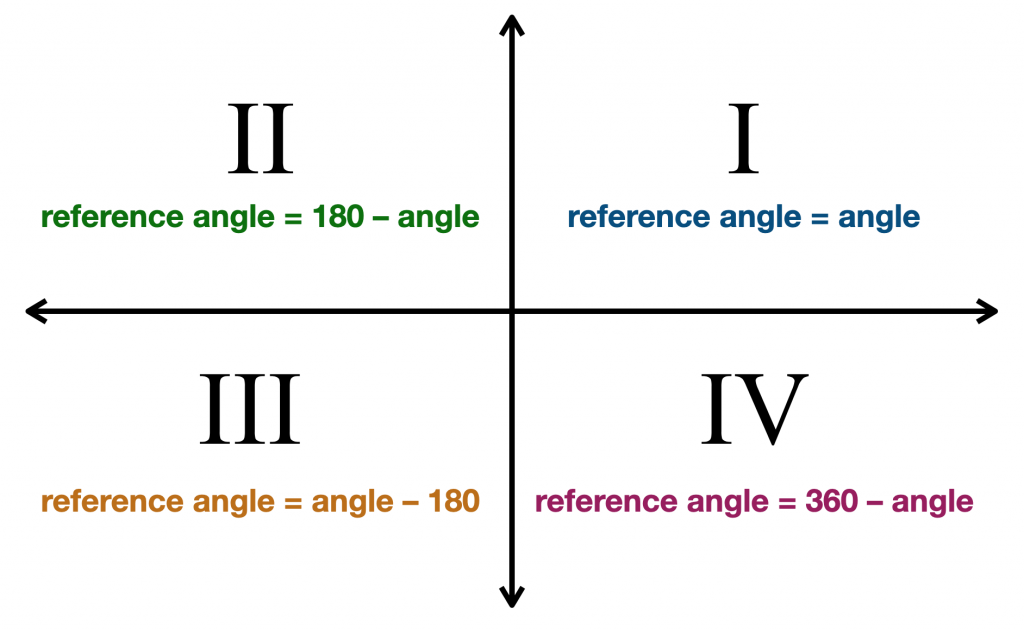
· And so, π radians is halfway around the circle, π/2 is a fourth of the way around the circle, so we'll do a conversion Let's draw an angle in standard position that measures 2π/3 radiansLearn how to draw an angle in radians in standard position in this video math tutorial by Mario's Math Tutoring We discuss how to sketch 3 different exampl · 0 to π/2 first quadrant, so reference angle = angle, π/2 to π second quadrant, so reference angle = π angle, π to 3π/2 third quadrant, so reference angle = angle π, 3π/2 to 2π fourth quadrant, so reference angle = 2π angle 10π/9 is a bit more than π


Reference Angle For An Angle Ex 2 Using Radians Youtube



Let S Learn The Unit Circle Angles In Standard Position Arc Length
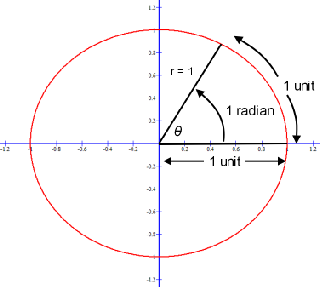
· RADIAN Another way to measure a central angle The intercepted arc has a length equal to the radius of the circle Measures the amount of rotation from the initial side to the terminal side of an angle The radian measure of a circle is 2 radians and a semicircle is è radians 1 radian r rPTS 2 REF a2 STA M2 TOP Radian Measure KEY radians 14 ANS 360 π 2⋅ 180 π = 360 π PTS 2 REF 0112a2 STA M2 TOP Radian Measure KEY degrees 15 ANS 2 8π 5 ⋅ 180 π = 2 PTS 2 REF a2 STA M2 TOP Radian Measure KEY degreesOne radian is the measure of the central angle of a circle such that the length of the arc between the initial side and the terminal side is equal to the radius of the circle A full revolution (360°) equals 2 π radians A half revolution (180°) is equivalent to π radians The radian measure of an angle is the ratio of the length of the arc subtended by the angle to the radius of the


Biomath Trigonometric Functions



Angles And The Unit Circle She Loves Math
Pretty much, yes if you want to be "nitpicky" about it, 314 radians = degrees In general, it's better to use pi instead of a rounded approximation like 314 or 22/7 or something like that By the way, 22/7 radians = degrees 2 commentsUsing τ = 2π Using π Formula Notes τ / 4 π / 2 1 / 4 of a circle (as an angle in radians) C = τr C = 2πr Circumference C of a circle of radius r A = τr 2 / 2 A = πr 2 Area of a circle Recall the area of a sector of angle θ (measured in radians) is A = θr 2 / 2;How do you convert 25 radians to degrees?



Trig Arclength And Radians



Trig Arclength And Radians
· Coterminal angle of 180° (π) 540°, 900°, 180°, 540° Coterminal angle of 195° 555°, 915°, 165°, 525° Coterminal angle of 210° (7π / 6) 570°, 930°, 150°, 510° Coterminal angle of 225° (5π / 4) 585°, 945°, 135°, 495° Coterminal angle ofIn trigonometry an angle is usually drawn in what is called the "standard position" as shown below In this position, the vertex of the angle (B) is on the origin of the x and y axis One side of the angle is always fixed along the positive xaxis that is, going to the right along the axis in the 3 o'clock direction (line BC)10 r ( x, y) θ O y x Definition 21 Trigonometric Functions of a General Angle Let θ be an angle in standard position and suppose that ( x , y ) is any point other than ( 0 , 0 ) on the terminal side of θ(Figure 23)If r = x2 y2 is the distance between ( x, y ) and ( 0 , 0 ), then the six trigonometric functions of θ are defined by Using similar triangles, you can see that the values



Trigonometry Angle Questions With Answers



Lesson Explainer Trigonometric Functions Values With Reference Angles Nagwa
Coterminal Angles Coterminal angles are angles in standard position (angles with the initial side on the positive x axis) that have a common terminal sideFor example 30 ° , − 330 ° and 390 ° are all coterminal To find a positive and a negative angle coterminal with a given angle, you can add and subtract 360 ° if the angle is measured in degrees or 2 π if the angle is measured inRelationship Between Radians and Degrees The circumference, C, of a circle of radius r is given by C = 2πr In a unit circle, r = 1, so C = 2πThis means that the arc length spanned by a complete revolution of 360 is 2π, so 360 = 2 π radiansCOTERMINAL ANGLES If you graph a 405° angle and a 45° angle in standard position on the same coordinate plane, you will notice that the terminal side of the 405° angle is the same as the terminal side of the 45° angle When two angles in standard position have the same terminal sides, they are called coterminal angles


Trigonometry Mathbook Of Carrabec High School Made By Students For Students


Angle Measure In Radians Geogebra
· Given an angle measure in degrees, draw the angle in standard position Express the angle measure as a fraction of 360° Reduce the fraction to simplest form Draw an angle that contains that same fraction of the circle, beginning on the positive xaxis and moving counterclockwise for positive angles and clockwise for negative anglesThis online calculator finds the quadrant of an angle in standard position The given angle may be in degrees or radians Use of calculator to Find the Quadrant of an Angle 1 Enter the angle in Degrees top input example 1250 in Radians second input as a fraction of π Example 27/5 π or 12 π then press the button "Find Quadrant" on the same row If you enter a quadrantal angle, theStandard Position An angle is in standard position if its vertex is located at the origin and one ray is on the positive xaxis The ray on the xaxis is called the initial side and the other ray is called the terminal side If the terminal side of an angle lies "on" the axes (such as 0º, 90º, 180º, 270º, 360º ), it is called a quadrantal angle



10 2 Angles And Their Measure Mathematics Libretexts


Biomath Trigonometric Functions
Converting between degrees and radians The angle corresponding to one complete rotation has measure 360 ° or 2π radians To convert from degrees to radians or radians to degrees we simply use the following conversion factors 2π radians = 360° or π radians = 180° For example, if we want to convert x° to y radians, we simply write,Lesson 41 –Angles in Standard Position & Radian Measure Math 2 Honors Santowski Math 2 Honors Santowski 2 terminal arm of an angle in standard position and the xaxis 60°/x = 180°/ πx = /3 radians 90°/x = 180°/ π x = π/2 radiansAngles measured in degrees, are shown with the symbol ° Subdivisions of the degree are minute (symbol ′, 1′ = 1/60°) and second {symbol ″, 1″ = 1/3600°} An angle of 360° corresponds to the angle subtended by a full circle, and is equal to 2π radians, or 400 gradians


General Angles And Radian Measure



Let S Learn The Unit Circle Angles In Standard Position Arc Length
Area of a Sector of a Circle For a circle of radius r, the area A of a sector of the circle with central angle θ is given by 1 2 2 ArT where θ is measured in radians Examples Find the area of the sector of the circle with radius r and central angle θ 1 r = 6 inches, θ = π/3 2 r = 25 feet, θ = 225Solution Given, 90 degrees is the angle Angle in radian = Angle in degree x (π/180) = 90 x (π/180) = π/2 Hence, 90 degrees is equal to π/2 in radian Radians to degrees Conversion As we have already discussed, how to convert degrees to radians for any specific angle Now, let us see how we can convert radians to degrees for any specific angleIdentify if x is the angle, or if x is the ratio (pay attention to the position it is in) b if the angle is given, find the approximate ratio using a calculator (can't use special triangles on nonspecial angles) if the ratio is given, find all possible approximate angles within first positive revolution 25 3 tan 8 x π = 26 tan 08x = − 27 3 sin 8 x = 28
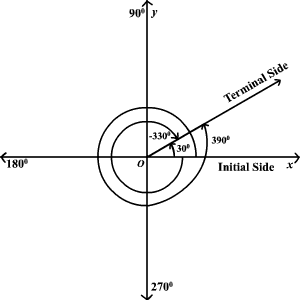


Coterminal Angles



Day 9 Hw 1 And 2 Find A Coterminal Angle Between 0 And 2 Pi Youtube
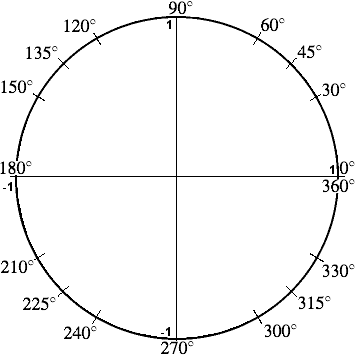


Trigonometry Facts The Amazing Unit Circle



Right Triangle Trigonometry


Working With Angles
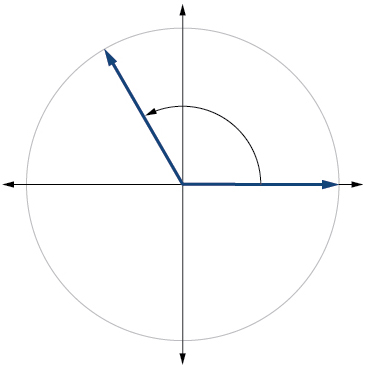


Angles Algebra And Trigonometry



Let S Learn The Unit Circle Angles In Standard Position Arc Length
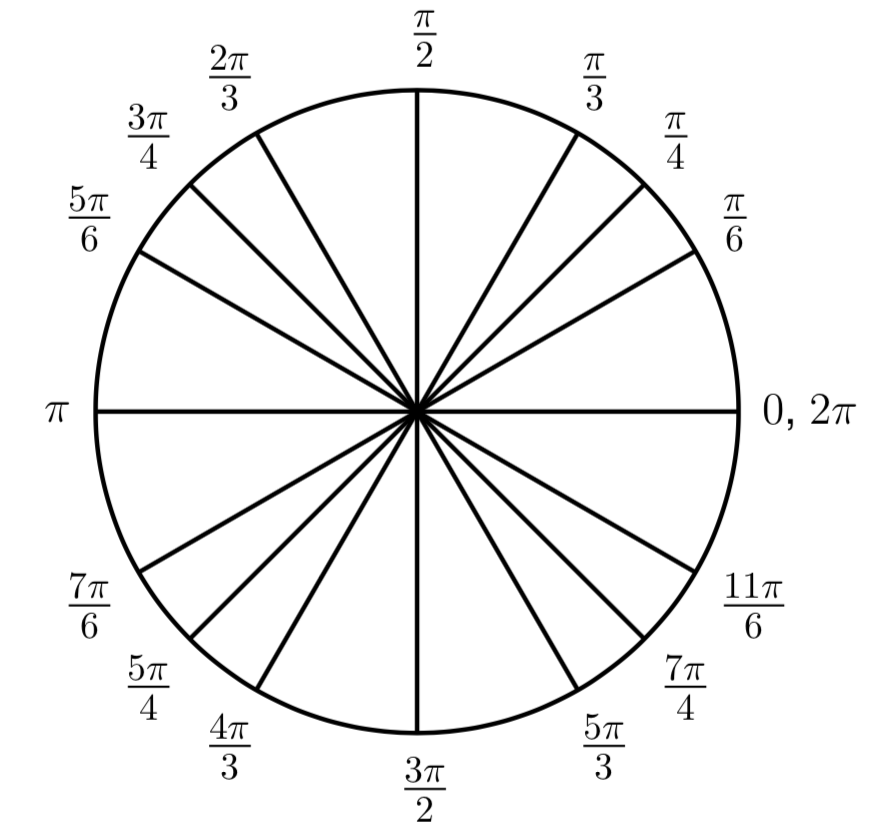


Mfg The Unit Circle



Solving Cos 2x Sin X 0 Within The Domain 0 2 Pi Why Am I Missing Some Solutions Mathematics Stack Exchange



Angles And Radian Measure Ppt Download


Radian Angles Quadrants Video Radians Khan Academy



Chapter 9 2 Jmap



Angles Math 126 Precalculus Openstax Cnx
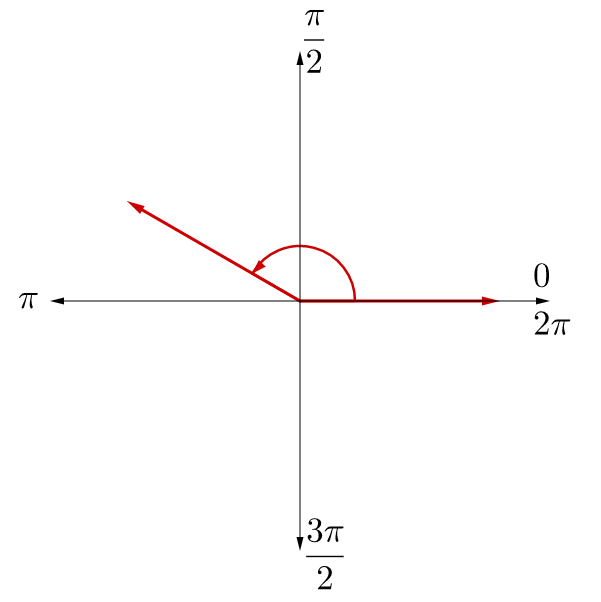


4 01 Angle Measures


The Measurement Of Angles



Steradian Wikipedia
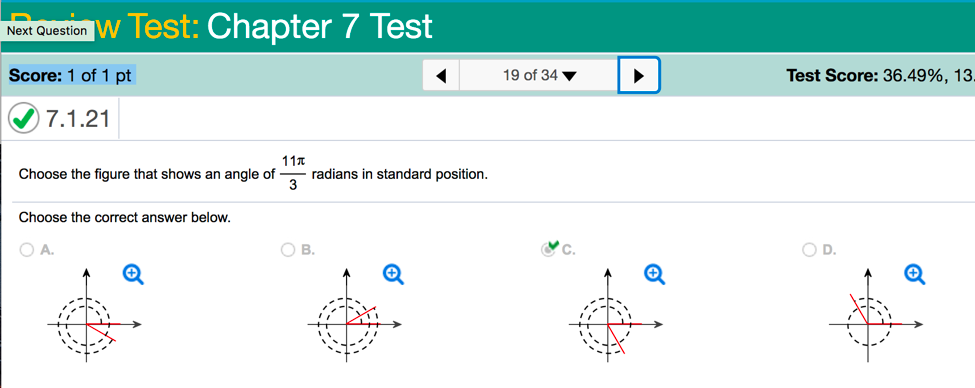


Solved Choose The Figure That Shows An Angle Of 11 Pi 3 R Chegg Com



What Quadrant Is The Terminal Side Of An Angle Of Measure 7pi 4 In Study Com



2 Radian Measure Dfracpi4 R See How To Solve It At Qanda
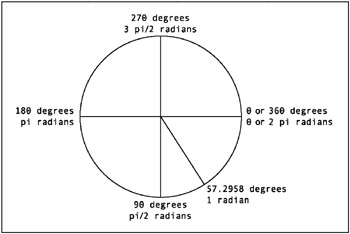


Angles Foundation Actionscript 3 0 Animation Making Things Move



Section 3 1 Radians And Angles In Standard Position Ppt Download



Angles And Their Radian Measure Ck 12 Foundation
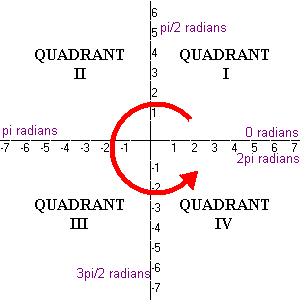


How Do You Determine The Quadrant In Which 6 02 Radians Lies Socratic


How Do You Find The Value Of Cot 2pi 3 Socratic


Webpage Of Dr Tom Cuchta
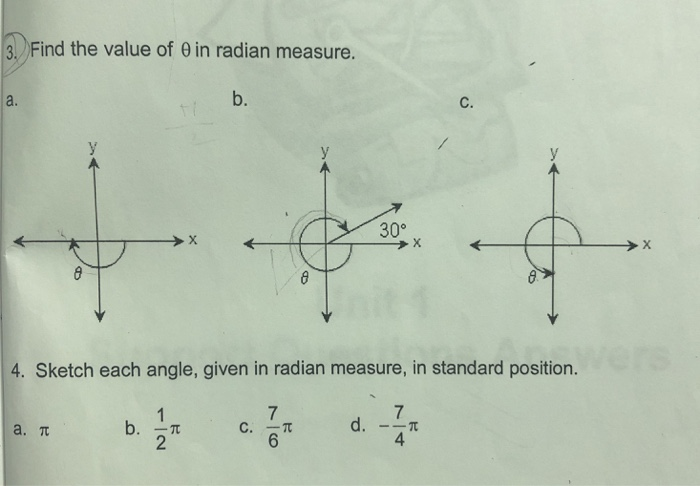


Solved Find The Value Of 8 In Radian Measure B S 300 4 Chegg Com
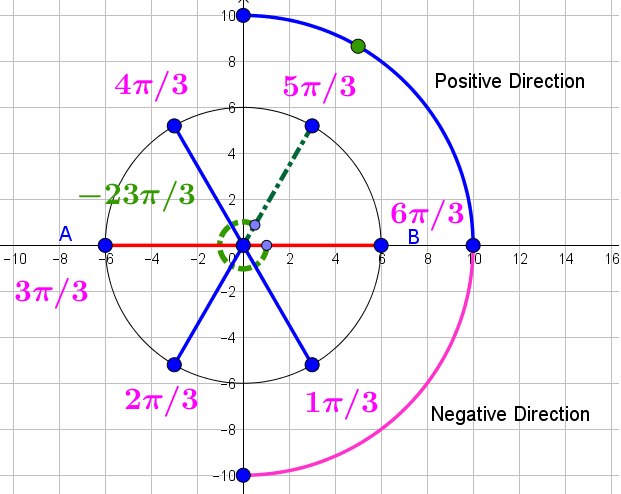


How Do You Sketch The Angle In Standard Position 23pi 3 Socratic
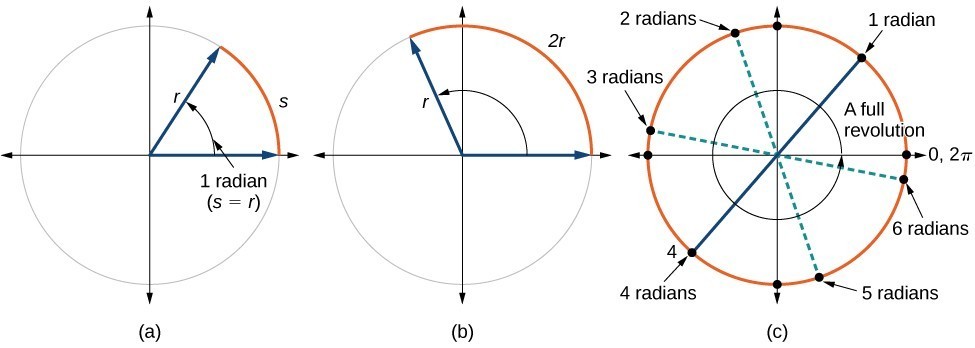


Angles Precalculus Ii



Apc The Sine And Cosine Functions


Tau Day No Really Pi Is Wrong The Tau Manifesto By Michael Hartl



Angles And The Unit Circle She Loves Math
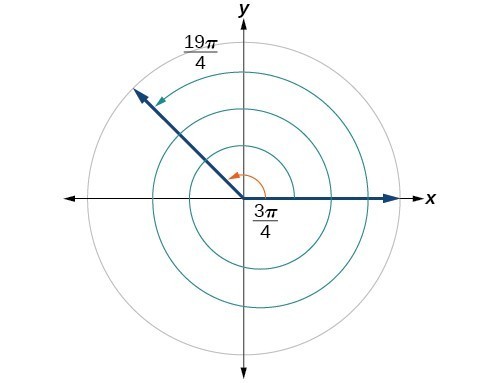


Cochranmath Coterminal And Reference Angles
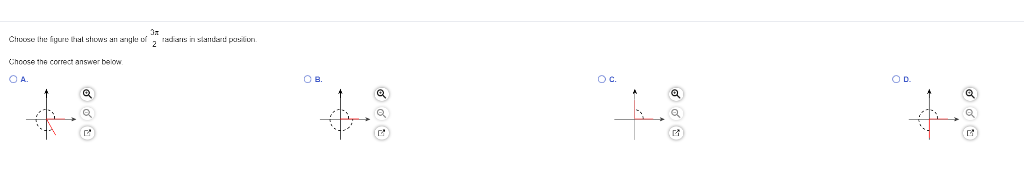


Solved Choose The Figure That Shows An Angle Of 3pi 2 Rad Chegg Com



10 2 Angles And Their Measure Mathematics Libretexts



Trigonometry


Radian Measure Including How To Convert Radians To Degrees And The Trigonometric Functions Of Special Angles



Measurement Of Angles
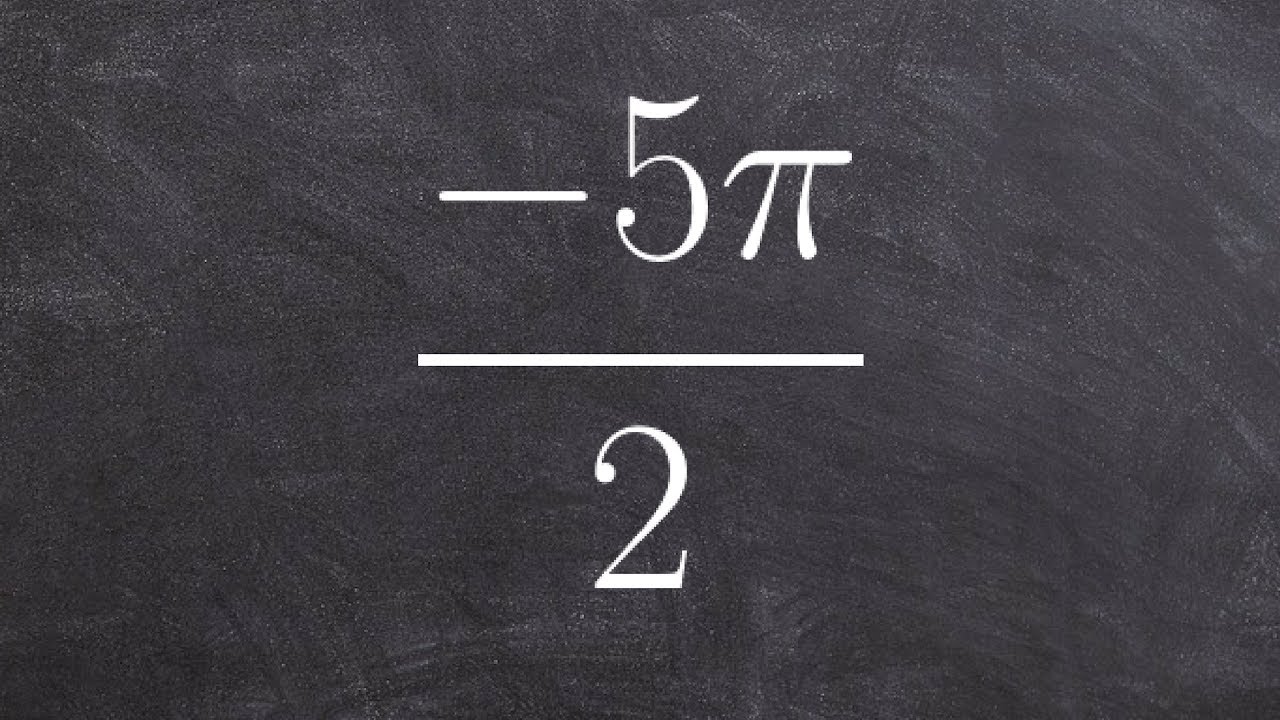


Sketch The Angle In Standard Position Youtube


Trigonometry Radian And Degrees


How To Find The Sin Pi 2 Value Using A Scientific Calculator Quora


4 01 Angle Measures
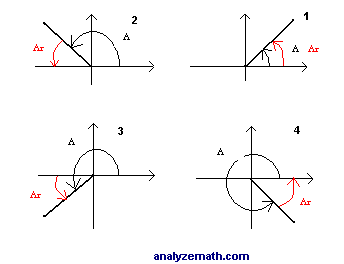


Find Reference Angle


Unit Circle Wyzant Lessons


4 01 Angle Measures



Trig Arclength And Radians
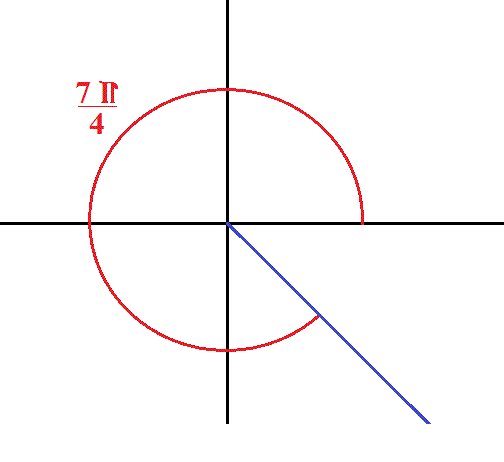


How Do You Sketch Theta 7pi 4 In Standard Position Socratic



1 1 Radian And Degree Measure Part 1



Objectives After Completing This Section You Should Be Able To Pdf Free Download



7 1 Angles Mathematics Libretexts



For The Angle Frac 33 Pi 5 A What Quadrant Does The Angle Frac 33 Pi 5 Fall In B Find Two Angles Coterminal To Frac 33 Pi 5 Measured In Radians One Positive And One Negative Find



Find The Reference Angle For 13 Pi 5 Study Com



How To Read Negative Radians In The Interval Mathematics Stack Exchange



Trigonometry Angle Questions With Answers



1 3 Arcs Angles And Calculators Mathematics Libretexts


Converting Between Radians And Degrees Expii


Content Radian Measure


Mfg The Unit Circle


Reference Angle Calculator Pi Day


Working With Angles In Degrees Radians Steemit



Solved Sketch Each Angle In Standard Position 2 Pi 3 B Chegg Com



Day 13 Cw Station 1 Finding A Coterminal Angle Between 0 And 2 Pi Youtube



Trig Arclength And Radians



Previous Answers Mcktrig7 316 Consider The Following Angle 340 A Draw The Course Hero



1 1 Radian And Degree Measure Part 1



Coterminal Angles Calculator Definition Formulas
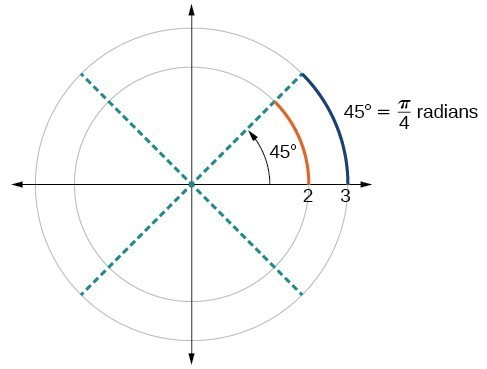


Angles Precalculus Ii



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿